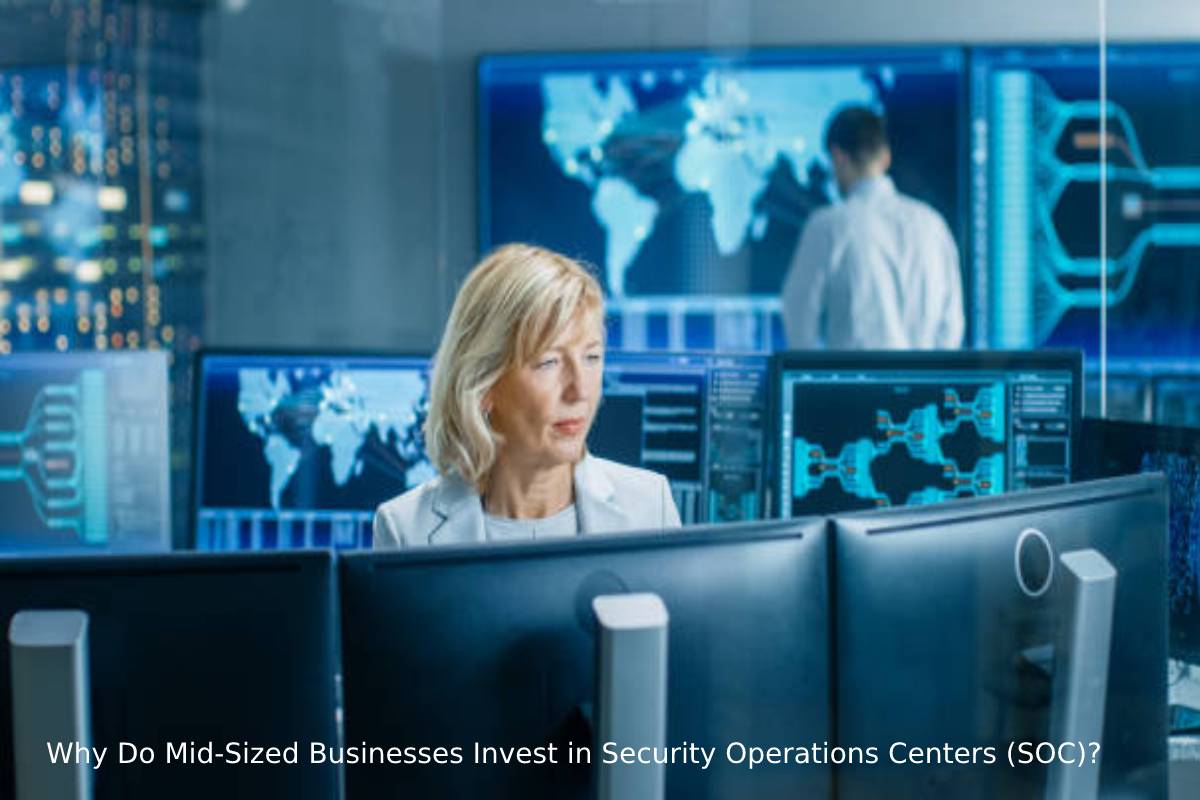
Small and mid-sized enterprises are confronted with a growing variety of risks worldwide. They want to locate security services that meet their budgets while still providing enough security. Lack of employees to create and operate their own SOC (Security Operation Centre) is a significant issue that SMBs (small and mid-sized organizations) confront. As a result, the SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) mechanism is no longer in effect. Many of these firms are eventually turning to outsource SOC as a Service to meet their security needs and improve their security posture.
Recent ransomware attacks indicate that hackers are focusing their efforts on small and mid-sized organizations, wreaking havoc since they lack competent SOC (Security Operations Centre) services. As a result, small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are scrambling to figure out how to deal with a slew of forthcoming issues. They seek reputable security service providers capable of implementing SOC as a Service.
Table of Contents
The key reasons to choose SOC:
The following are the main reasons to choose (SOC):
- Recognize that the cyber security situation has shifted dramatically – Contrary to popular assumption, small businesses are the target of the majority of cybersecurity threats. Furthermore, 60% of individuals who are afflicted will fail within six months.
- Awareness that legal landscapes are changing – Not only are the sorts of cyber security offenses changing, but so are the consequences for non-compliance with data protection laws.
- Improved reaction time — Internal security monitoring can be a time-consuming process. It can be challenging for in-house IT to keep up with the daily influx of warnings. Artificial intelligence and automation, available 24 hours a day, seven days a week, can be employed to their maximum potential.
How Can SMBs Protect Their Networks?
With the assistance of adequate IT infrastructure support, an SMB can protect itself by deploying solutions with cyber security in mind. This means that the systems they use should have features that allow them to encrypt data, authenticate users, and grant access.
Encrypting data on a network helps SMBs safeguard private and sensitive data while also improving the security of communication between clients and servers. Even if an unauthorized person or entity has access to encrypted data, it cannot be read without the necessary key. The next concern is how to manage access to those encryption keys, and the solution is to use authentication.
Authentication can take several forms. Username/password combinations, tokens, and other approaches are used on the client-side, whilst certificates are used on the server-side to identify trusted third parties. IT infrastructure solutions enable SMBs first to identify the authenticity of the user, server, or client app is who it claims to be and then confirm whether and how that entity should access a system, including the ability to decrypt encrypted data.
When IT infrastructure solutions include authorization capabilities, administrators can limit the scope of activity in their systems by granting special access permissions to groups or individuals for resources, data, or applications. Administrators can fine-tune the level of access allowed to each individual by specifying privileges. This helps administrators find a balance between giving employees the access privileges they need to accomplish their jobs effectively while also ensuring that they minimize the dangers of a data breach. This improves the security of not only the physical system as a whole but also the security of other systems that are connected to it.
Choosing a Smart Security Provider
One can follow the below checklist that guides the search for a comprehensive SOC service.
1. Complexity level
According to a recent Gartner analysis, MDR (managed detection and response) is a fast-growing sector. Although detection is essential for recognizing risks, the SOC should also provide prevention and IR (incident response) in the event of a disaster.
When considering a SOC, all one needs is a complete security package that includes decisive and effective IR, protection from DDoS attacks, ransomware, data breach, and disaster recovery. SOC should not be used if the provider does not provide 24/7 SOC and IR services.
2. Real-Time Threat Analysis
Monitoring threats in real-time with detection services and forensics is critical for the SOC. The security team’s small staff cannot handle the noisy and complex SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tools. They are unable to filter out false alarms, and as a result, their performance in critical security matters falls short.
3. Armed Threat Hunting
Staying armed necessitates that the network prepares in advance and actively searches for threats. This would result in the network automatically adjusting to the most recent cyber-attacks, which could have occurred only a few hours ago. The security specialists bear a great deal of responsibility in this regard. It necessitates learning the various and unique requirements of the client’s network and hunting down threats that can still pass through the detection process. To make this method work, one needs to adopt relevant and sufficient threat-intelligence sources, machine learning techniques, and a careful selection of everything that can help identify valid threats.
4. Compliance Control
Every SOC should comply with standards such as PCI DSS, HITECH, HIPAA, GLBA, FFIEC, and others that the high-quality industries must adhere to. Compliance organizations must provide templates for recommended security checks and vulnerability assessments and monitor whether businesses are adhering to the regulatory measures in place. Not only can hackers cost you a lot of money, but failing to meet required compliances can also result in penalties!
5. Strategic Advising
The security engineers will gain an in-depth understanding of the company’s network after monitoring it and hunting for potential threats. This knowledge of network topology and the locations of vital assets will assist them in protecting those with a proper defense strategy. The outsourced SOC provider helps with designing and improving security posture.
Instead of having scalable cloud-based technology, a well-defined IR (Incident Response) process and a team of well-trained security specialists will persuade clients to gain insight into their organization’s security posture. Furthermore, this aids in the improvement and efficient operation of business processes.
6. Defined Pricing
The SOC service provider should make fixed pricing plans. The rates shall vary on the number of sensors and users instead of log data’s volume and servers monitored. Such predictable and defined pricing models are essential for small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs). These organizations struggle with fluctuating costs and can’t afford costly managed services. Therefore, the SOC providers should not have unpredictable costs.
Final Thoughts
Mid-size businesses have found a cost-effective solution to address their ransomware attacks. Considering the above factors makes it easier to decide to outsource the SOC provider without compromising on safety.